The BAG information portal on communicable diseases publishes updated infection data for Switzerland and the Principality of Liechtenstein every Wednesday.
Last week’s update continues to show high activity of Influenza A and RSV.
👉 https://www.idd.bag.admin.ch
Both are enveloped viruses and highly relevant in healthcare settings. The key point is not only whether disinfection is performed – but with what.
Alcohol-based disinfection: why it is so central
In hand hygiene, alcohols are the backbone of effective disinfection. The main active substances used are:
- Ethanol
- n-Propanol (propan-1-ol)
- Isopropanol (propan-2-ol)
as well as targeted combinations of these.
These agents act through multiple mechanisms simultaneously:
- Denaturation of proteins
- Damage to cell membranes and viral envelopes
- Inactivation of essential microbial structures
As a result, alcohols are highly effective against a broad spectrum of pathogens – both bacterial and viral.
Bacteria, fungi and viruses: the spectrum of activity matters
For hygienic hand disinfection, the decisive factor is the spectrum of activity covered by a product:
- bactericidal, including tuberculocidal / mycobactericidal
- levurocidal, fungicidal
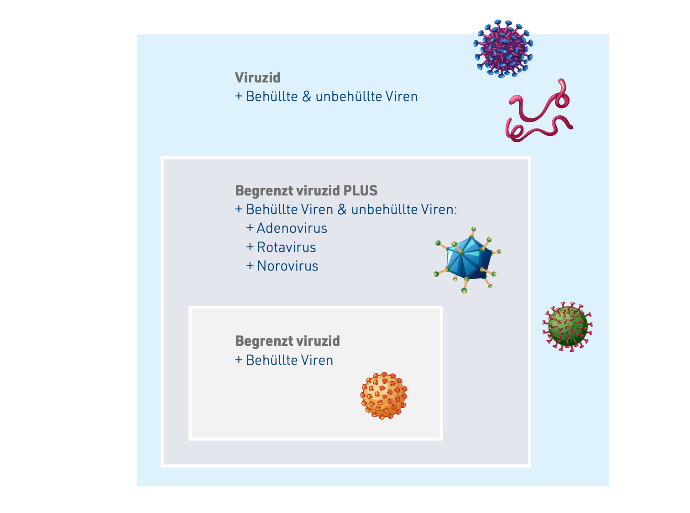
virucidal, differentiated as:
- limited virucidal → enveloped viruses (e.g. Influenza A, RSV)
- limited virucidal PLUS → additionally Adeno-, Rota-, Noroviruses
- virucidal → all enveloped and non-enveloped viruses
Influenza A and RSV fall within the limited virucidal category. Modern alcohol-based formulations reliably achieve this spectrum – often exceeding it.